
QUENCH
A research program on reflood of an overheated core and corresponding topics is running at KIT, including large scale bundle tests at IAM-WPT , various kinds of separate-effects tests at IAM-AWP , model development and code application.
STRESA was developed by JRC-Ispra in the year 2000 with the main objective to disseminate documents and experimental data from large in-house JRC scientific projects, and has been extensively used in order to provide a secure repository of experimental data.

At present time the JRC is engaged in the management of this new version of the STRESA tool to secure the European Union storage for severe accident experimental data and calculations.
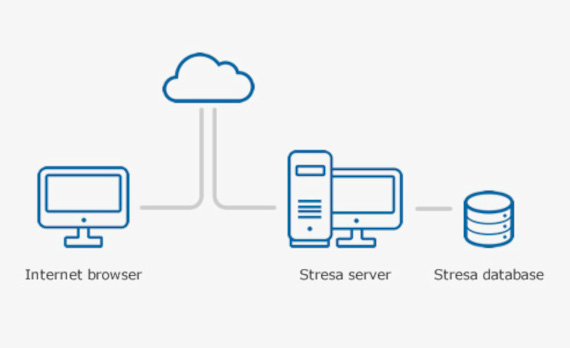
Only registered users may access and make use of the features available in this new version of STRESA. If you are already registered, just login using your ECAS credentials and start using the information system.
If you are not registered yet, or you are having troubles with the login, please contact the administrator.