MOZART
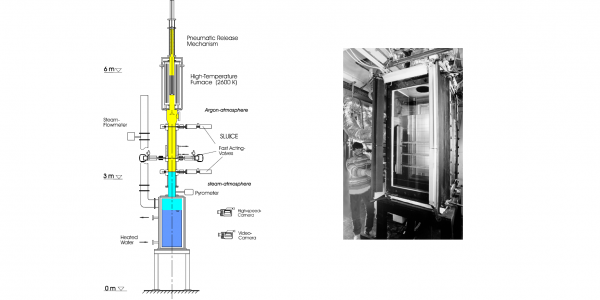
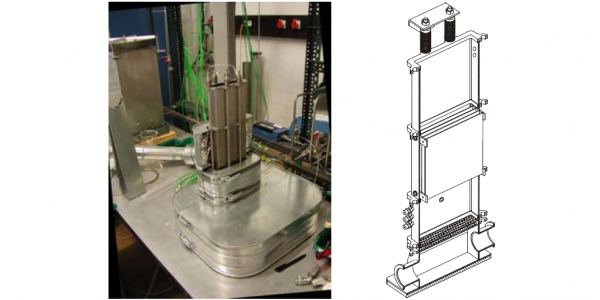
The Mozart analytical test program, conducted from 2005 to 2007, was dedicated to the study of oxidation in air of nuclear fuel cladding. This study was part of the International Source Term Program initiated by the IRSN, whose aim is to reduce uncertainties concerning the evaluation of radioactive product emissions into the environment in the event of a core meltdown accident in a pressurized water reactor or a spent fuel storage pool accident.